(Image credit- Smartprix) Designed to reduce en...
news-extra-space
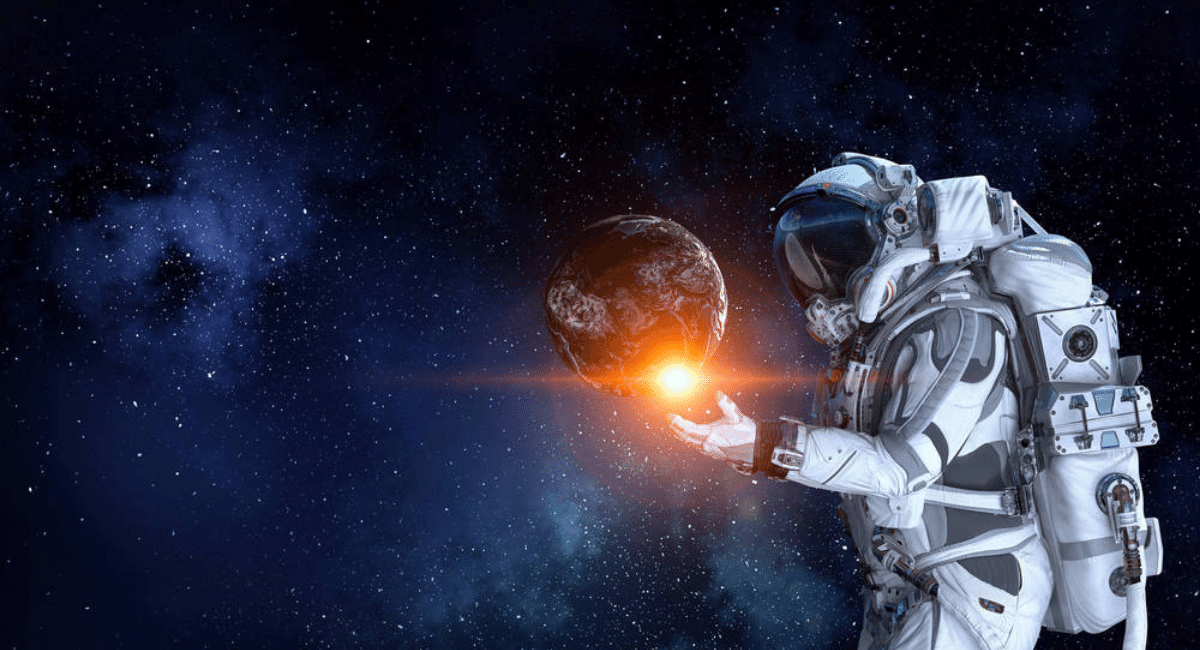

 Mutations like this can be brought about by openness to an overabundance of bright radiation and different types of radiation, including chemotherapy. For this situation, scientists are dubious that the mutations might have come about because of space radiation. However, astronauts work in an outrageous environment where many elements can bring about substantial mutations, in particular space radiation, and that implies there is a gamble that these mutations could form into clonal hematopoiesis, said lead creator David Goukassian, teacher of medication at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, in a statement.
The subject of astronaut wellbeing is more relevant than at any time in recent memory. Simply last year, NASA proposed to change as far possible its astronauts can be presented to safeguard their well-being. Moreover, the agency is attempting to permit younger astronauts to be presented to moderately higher radiation measures than more established astronauts, killing the distinctions in limits among men and women.
Mutations like this can be brought about by openness to an overabundance of bright radiation and different types of radiation, including chemotherapy. For this situation, scientists are dubious that the mutations might have come about because of space radiation. However, astronauts work in an outrageous environment where many elements can bring about substantial mutations, in particular space radiation, and that implies there is a gamble that these mutations could form into clonal hematopoiesis, said lead creator David Goukassian, teacher of medication at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, in a statement.
The subject of astronaut wellbeing is more relevant than at any time in recent memory. Simply last year, NASA proposed to change as far possible its astronauts can be presented to safeguard their well-being. Moreover, the agency is attempting to permit younger astronauts to be presented to moderately higher radiation measures than more established astronauts, killing the distinctions in limits among men and women.
 The blood samples for this most recent review were gathered from 12 male and two female astronauts ten days before their flight and upon arrival. The samples were then cryogenically put away at - 112 degrees Fahrenheit for about twenty years.
The mutations in the blood samples look like the sort of physical mutations we see in more seasoned people — which is fascinating all alone, taking into account that the middle age of the astronauts was just 42. Moreover, NASA has not launched a rocket to take astronauts to the Moon, nor has it selected a crew that will study the Moon’s surface under its Artemis Program.
Albeit the clonal hematopoiesis we noticed was of moderately tiny size, the way that we noticed these mutations was terrific given the somewhat young age and strength of these astronauts, Goukassian said.
The blood samples for this most recent review were gathered from 12 male and two female astronauts ten days before their flight and upon arrival. The samples were then cryogenically put away at - 112 degrees Fahrenheit for about twenty years.
The mutations in the blood samples look like the sort of physical mutations we see in more seasoned people — which is fascinating all alone, taking into account that the middle age of the astronauts was just 42. Moreover, NASA has not launched a rocket to take astronauts to the Moon, nor has it selected a crew that will study the Moon’s surface under its Artemis Program.
Albeit the clonal hematopoiesis we noticed was of moderately tiny size, the way that we noticed these mutations was terrific given the somewhat young age and strength of these astronauts, Goukassian said.
 The presence of these mutations doesn't be guaranteed to imply that the astronauts will foster cardiovascular infection or malignant growth, he added. But, in any case, there is the gamble that, after some time, this could occur through continuous and delayed openness to the outrageous environment of deep space. Hence, Goukassian and his group are recommending that NASA ought to evaluate astronauts for these sorts of mutations routinely.
Researchers have long estimated the various well-being takes a chance with astronauts face. But, at the same time, investing expanded energy times in space — and the more we find, the better we can guarantee their security over the long haul.
The presence of these mutations doesn't be guaranteed to imply that the astronauts will foster cardiovascular infection or malignant growth, he added. But, in any case, there is the gamble that, after some time, this could occur through continuous and delayed openness to the outrageous environment of deep space. Hence, Goukassian and his group are recommending that NASA ought to evaluate astronauts for these sorts of mutations routinely.
Researchers have long estimated the various well-being takes a chance with astronauts face. But, at the same time, investing expanded energy times in space — and the more we find, the better we can guarantee their security over the long haul.
Leave a Reply






