In the ever-changing world of technology and retai...
news-extra-space
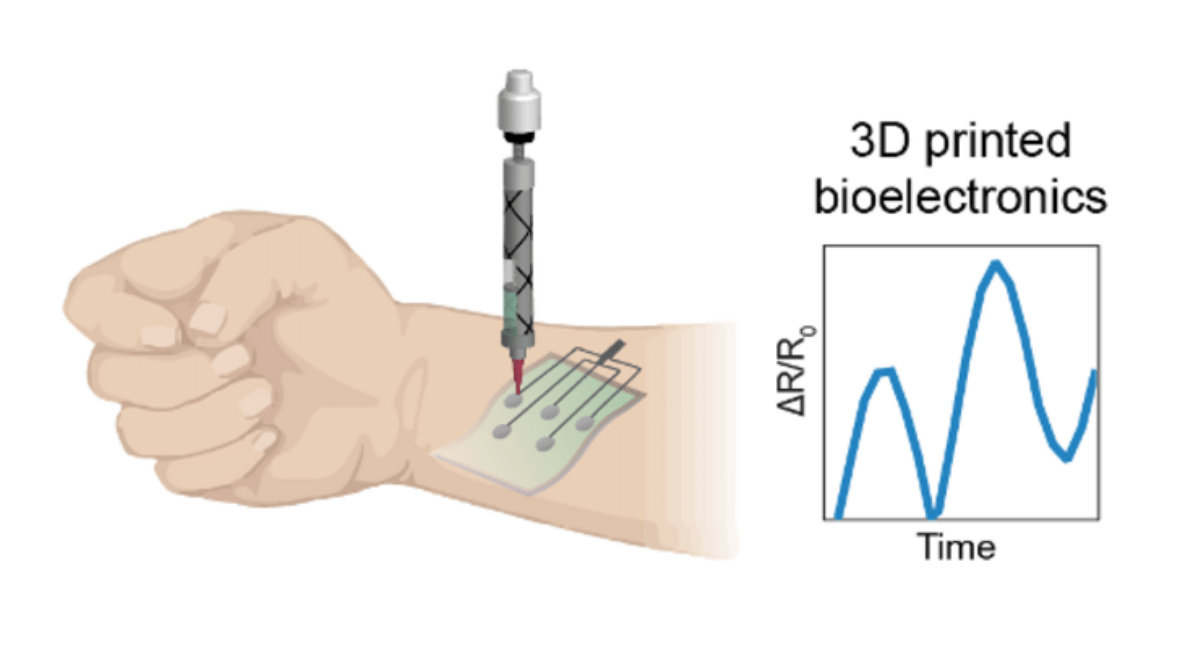
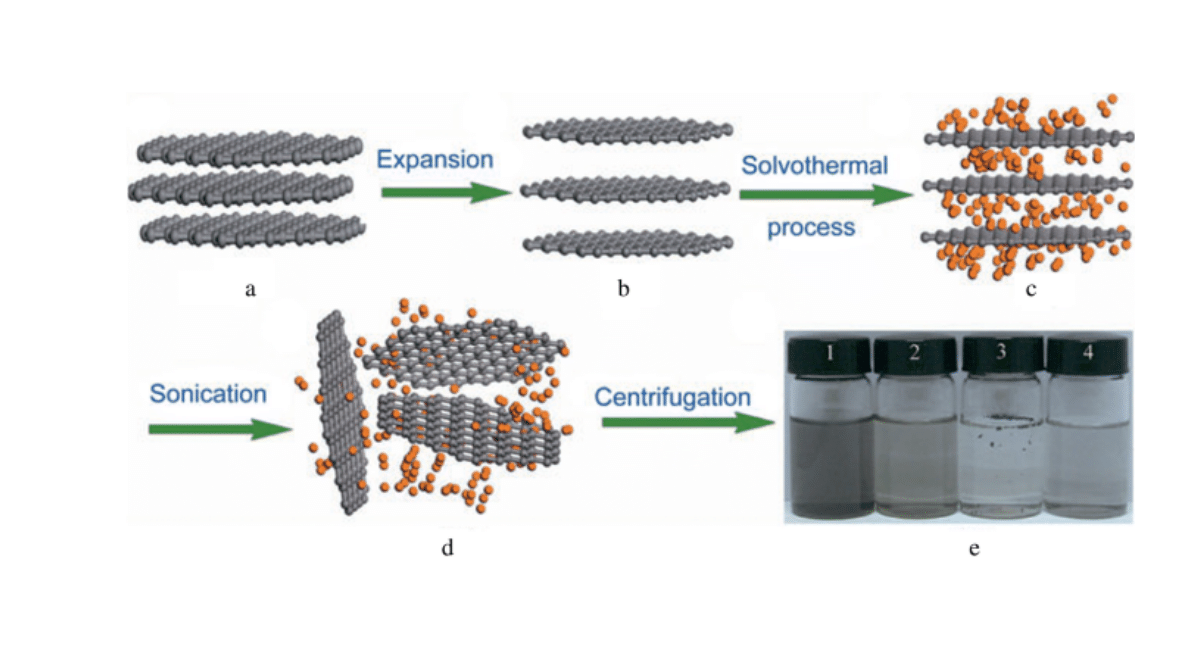
 Texas A&M University researchers have developed a new class of biomaterial inks that mimic the properties of highly conductive human tissue, similar to pores and skin, that make them ideal for 3D printing. However, the biomaterial inks like this one use molybdenum disulfide MoS2, a new class of 2D nanomaterial. As a result of the thin layers of MoS2, it has chemical energy and can be combined with the gelatin to make a flexible hydrogel similar to that of Jell-O.
Texas A&M University researchers have developed a new class of biomaterial inks that mimic the properties of highly conductive human tissue, similar to pores and skin, that make them ideal for 3D printing. However, the biomaterial inks like this one use molybdenum disulfide MoS2, a new class of 2D nanomaterial. As a result of the thin layers of MoS2, it has chemical energy and can be combined with the gelatin to make a flexible hydrogel similar to that of Jell-O.
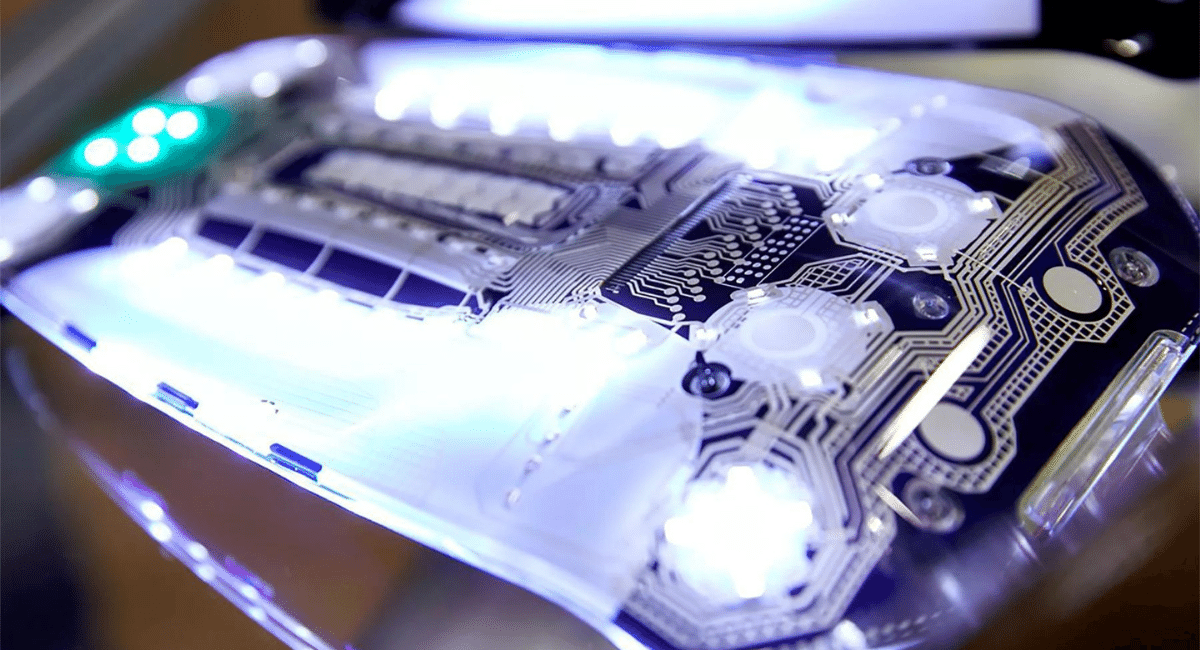
 This work is significant in 3D printable printing, stated Akhilesh Gaharwar, an affiliate professor within the Division of Biomedical Engineering. The new hydrogel ink is highly biocompatible and electrically conductive, paving the way for implantable and wearable bioelectronics in the future."
As pressure increases, the ink's viscosity decreases. So, it floats more like a liquid when squeezed, like ketchup or toothpaste, which has shear-thinning properties. To produce a hydrogel ink that can be used to print 3D objects, the team integrated electrically conductive nanomaterials into modified gelatin.
This work is significant in 3D printable printing, stated Akhilesh Gaharwar, an affiliate professor within the Division of Biomedical Engineering. The new hydrogel ink is highly biocompatible and electrically conductive, paving the way for implantable and wearable bioelectronics in the future."
As pressure increases, the ink's viscosity decreases. So, it floats more like a liquid when squeezed, like ketchup or toothpaste, which has shear-thinning properties. To produce a hydrogel ink that can be used to print 3D objects, the team integrated electrically conductive nanomaterials into modified gelatin.
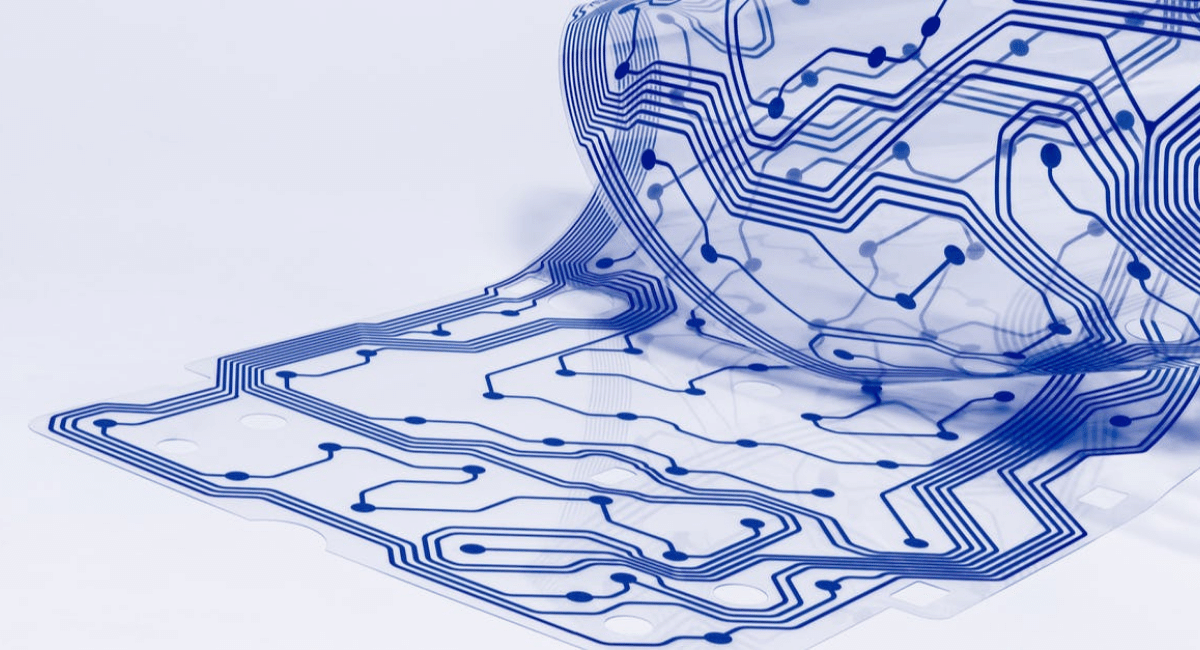 Despite being extremely elastic, these 3D-printable devices are not susceptible to breaking, according to Kaivalya Deo, a graduate student in the biomedical engineering department and lead author of the paper. In addition, these devices are electronically active, which allows them to monitor dynamic human motion continuously.
Researchers at the Gaharwar Laboratory designed a multi-head 3D bioprinter that is economical, open-source, and completely customizable, using open-source tools and freeware. Additionally, researchers can build 3D bioprinters customized to meet their own research needs.
Hydrogel ink can be used to print electrically conductive circuits in 3D and is not limited to planar designs, allowing researchers to customize bioelectronics according to patient needs.
Despite being extremely elastic, these 3D-printable devices are not susceptible to breaking, according to Kaivalya Deo, a graduate student in the biomedical engineering department and lead author of the paper. In addition, these devices are electronically active, which allows them to monitor dynamic human motion continuously.
Researchers at the Gaharwar Laboratory designed a multi-head 3D bioprinter that is economical, open-source, and completely customizable, using open-source tools and freeware. Additionally, researchers can build 3D bioprinters customized to meet their own research needs.
Hydrogel ink can be used to print electrically conductive circuits in 3D and is not limited to planar designs, allowing researchers to customize bioelectronics according to patient needs.
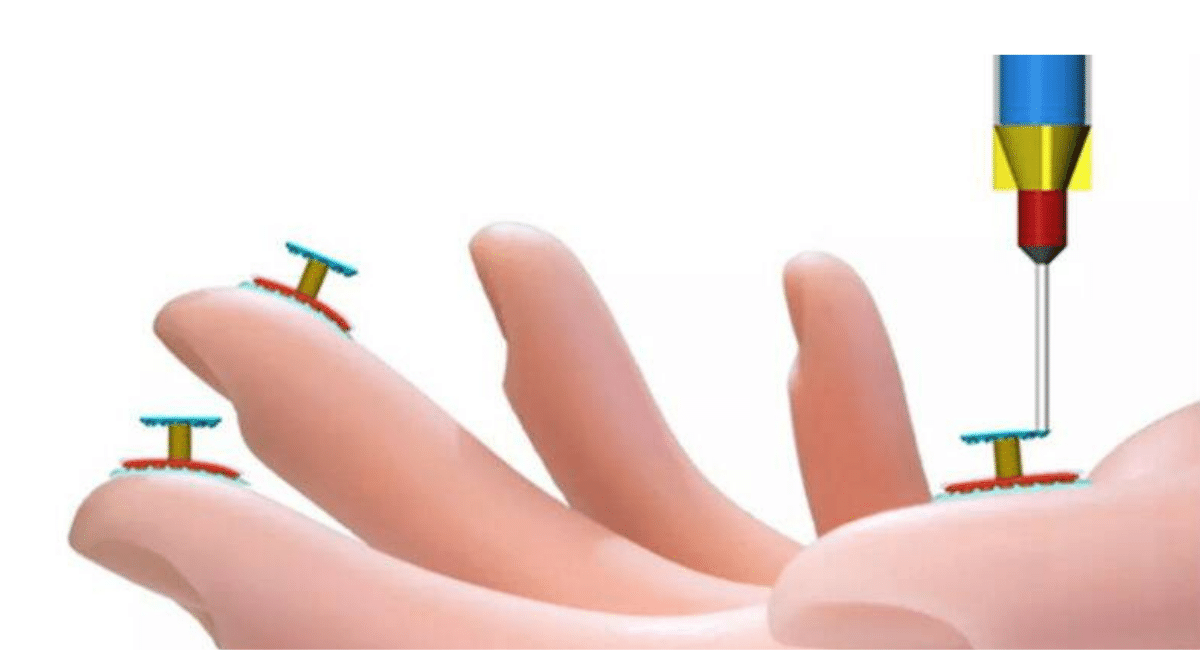 This 3D printer allowed Deo to print electrically active and stretchable digital gadgets. These gadgets show extraordinary strain-sensing capabilities and can be utilized for engineering customizable monitoring methods. In addition, you can access new potentialities for versatile designing sensors fitted with built-in electronics.
Moreover, the potential functions of brand new ink are in 3D printing digital tattoos for people who suffer from illness with Parkinson’s disease. However, the researcher said this printed e-tattoo quickly detects the affected person’s motion and tremor.
This 3D printer allowed Deo to print electrically active and stretchable digital gadgets. These gadgets show extraordinary strain-sensing capabilities and can be utilized for engineering customizable monitoring methods. In addition, you can access new potentialities for versatile designing sensors fitted with built-in electronics.
Moreover, the potential functions of brand new ink are in 3D printing digital tattoos for people who suffer from illness with Parkinson’s disease. However, the researcher said this printed e-tattoo quickly detects the affected person’s motion and tremor.
Leave a Reply






