Image credit : Hackster.io ...
news-extra-space
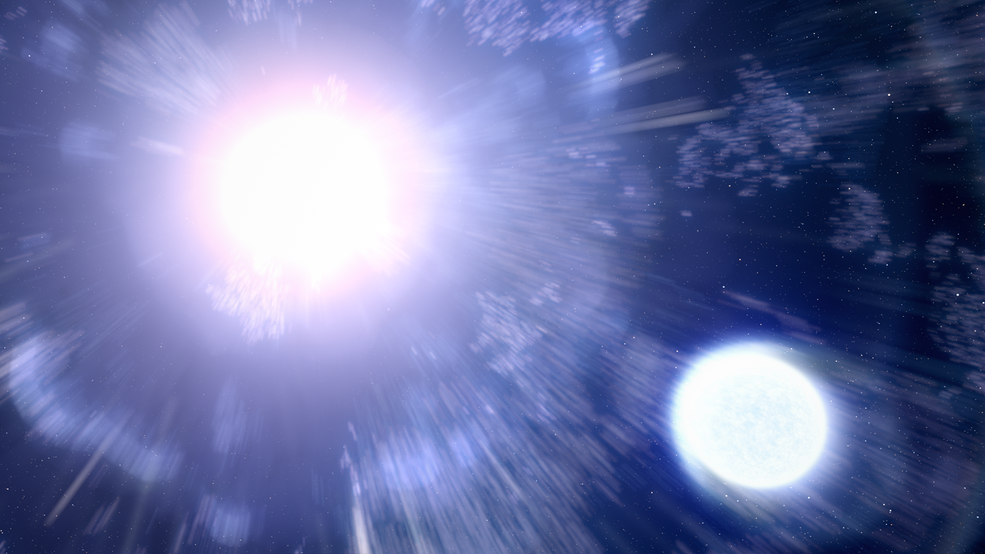

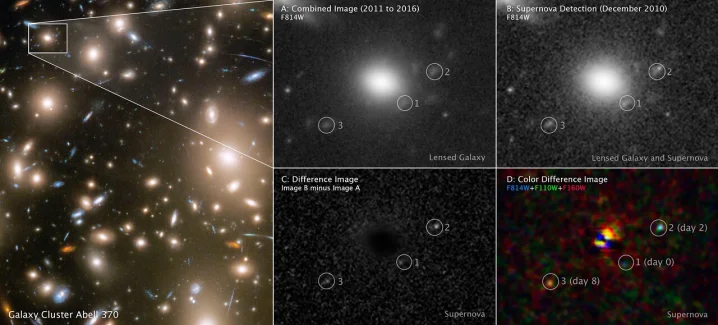 Due to a phenomenon known as gravitational lensing, in which a large object is placed between us and the object being examined, it was possible to see three different moments in time. If the intermediary object is large enough, its gravitational pull will warp space, altering how the thing behind it appears. When the intermediary object serves as a magnifying glass, the background object may appear brighter and may also appear at a different location in space depending on how the light of the background object has been twisted. Since the light from the explosion in this instance was bent along three distinct pathways with various lengths, Hubble was able to see three distinct occurrences.
The supernova is incredibly old and far away; it is thought to have occurred 11 billion years ago, which is not far from the universe's beginning, 13.8 billion years ago. One of the first supernovae ever seen in such clarity, scientists were able to determine the size of the star by comparing three separate time frames in the photograph. The star is a red supergiant, which are stars that are around 500 times as massive as the sun.
The study has been made public in the journal Nature.
Due to a phenomenon known as gravitational lensing, in which a large object is placed between us and the object being examined, it was possible to see three different moments in time. If the intermediary object is large enough, its gravitational pull will warp space, altering how the thing behind it appears. When the intermediary object serves as a magnifying glass, the background object may appear brighter and may also appear at a different location in space depending on how the light of the background object has been twisted. Since the light from the explosion in this instance was bent along three distinct pathways with various lengths, Hubble was able to see three distinct occurrences.
The supernova is incredibly old and far away; it is thought to have occurred 11 billion years ago, which is not far from the universe's beginning, 13.8 billion years ago. One of the first supernovae ever seen in such clarity, scientists were able to determine the size of the star by comparing three separate time frames in the photograph. The star is a red supergiant, which are stars that are around 500 times as massive as the sun.
The study has been made public in the journal Nature.
Leave a Reply






