Study portrays surprising differences in brains of modern humans & Neanderthals
September 09, 2022 By Awanish Kumar
(Image Credit Google)
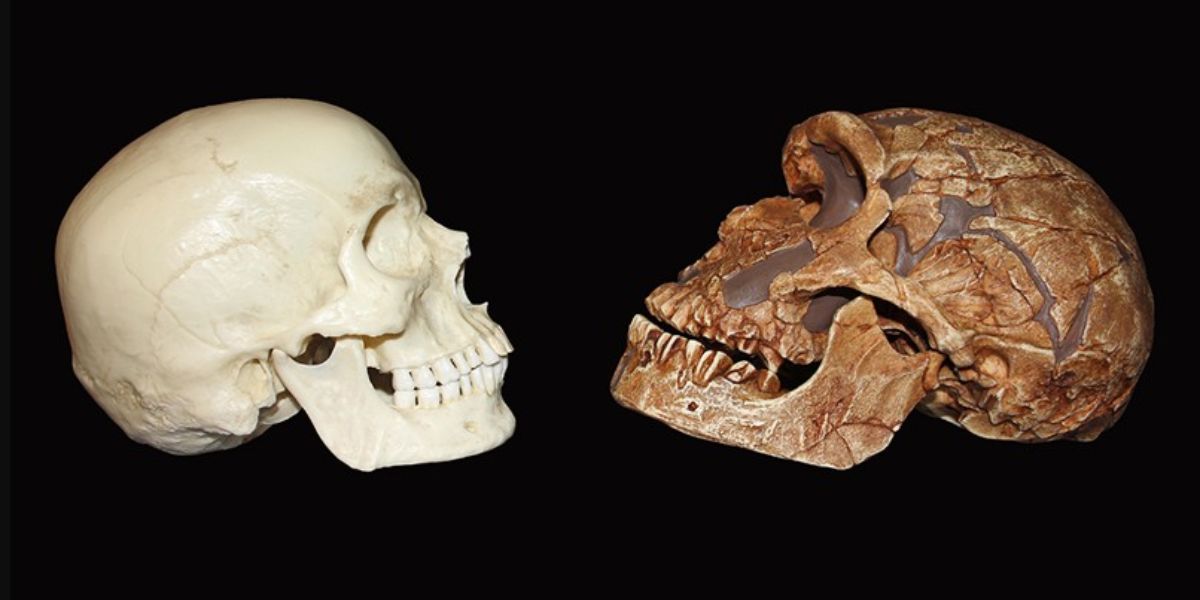
The ancestors of Neanderthals and modern humans were traveling across the globe more than 500,000 years ago when a critical genetic mutation led part of their brains to abruptly develop. According to a study published in Science1, this mutation significantly enhanced the number of brain cells in the ancestors of modern humans, providing them a cognitive advantage over their Neanderthal relatives.
“This is a surprisingly important gene,” says Arnold Kriegstein, a neurologist at the University of California, San Francisco. He anticipates that it will instead prove to be just one of numerous genetic modifications that give humans an evolutionary edge over other hominins. I believe it offers a completely fresh perspective on human evolution.
Cognitive advantage
One gene stood out to neuroscientists Wieland Huttner and Anneline Pinson at the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics in Dresden, Germany. The TKTL1 gene produces a protein throughout the early stages of a fetus's brain development. A single genetic alteration in the human version of TKTL1 altered one amino acid, creating a protein distinct from those present in Neanderthals, non-human primates, and the ancestors of modern humans.
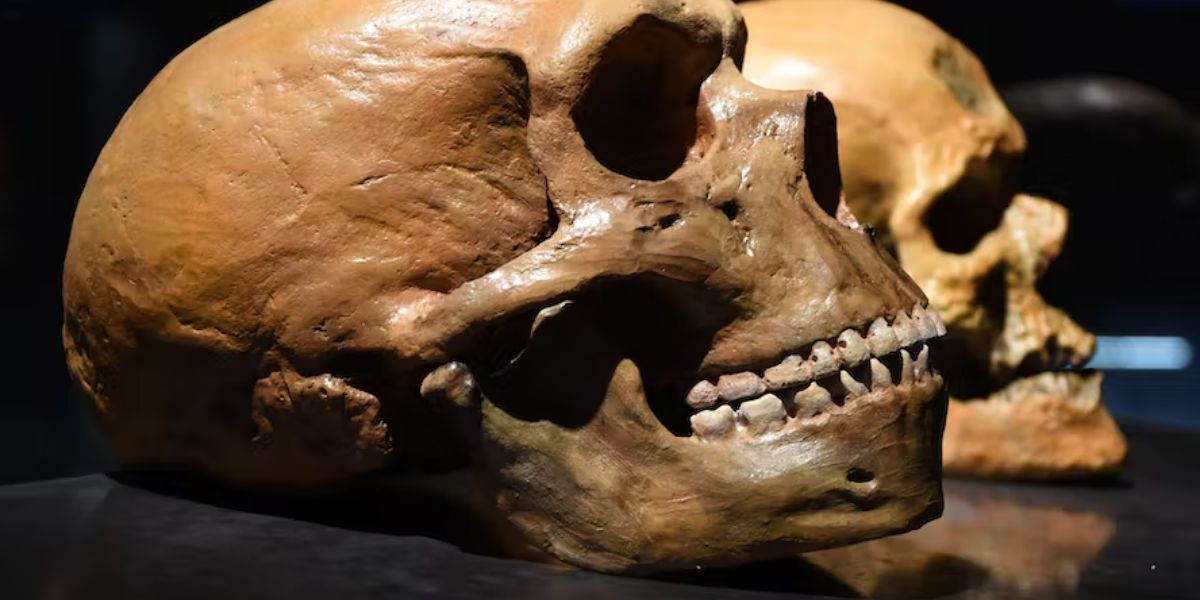

Pinson and her team put mouse and ferret embryonic brains, either the human or ancestral version of TKTL1 to test this. The number of brain progenitor cells in the mice with the human gene was substantially higher. The fetal tissue produced fewer progenitor cells and neurons than it typically would when the researchers synthesized neocortex cells from a human fetus to create the ancestral version. The same held true when they implanted the ancestor form of TKTL1 into brain organoids, tiny structures made from human stem cells that resemble the human brain.
Brain size
Given that Neanderthal and human brains appear to have been around the same size in fossil records, modern humans' neocortices are either denser or occupy a more significant part of the brain. Huttner and Pinson state that they were taken aback by how profoundly such a minor genetic alteration could effect neocortex development. Huttner claims that the mutation was a serendipitous one that had significant effects.
More skeptical is the University of California, San Diego neuroscientist Alysson Muotri. He makes the observation that various cell lines behave in various ways when created into organoids and wants to see the ancestral form of TKTL1 investigated in more human cell types. Additionally, he notes that the original Neanderthal genome was compared to that of a contemporary European; this suggests that Neanderthals and human populations in other regions of the world may share certain genetic variations.
According to Pinson, the Neanderthal variant of TKTL1 is extremely uncommon in contemporary humans, and it is unknown whether it results in any illnesses or cognitive abnormalities. According to Huttner, the only way to demonstrate that it plays a part in cognitive function would be to genetically modify mice or ferrets such that they always carry the human form of the gene and compare their behavior to that of animals that carry the ancestral form. According to Pinson, she now intends to investigate in further detail the methods by which TKTKL1 promotes the development of new brain cells.
By Awanish Kumar
I keep abreast of the latest technological developments to bring you unfiltered information about gadgets.


 Pinson and her team put mouse and ferret embryonic brains, either the human or ancestral version of TKTL1 to test this. The number of brain progenitor cells in the mice with the human gene was substantially higher. The fetal tissue produced fewer progenitor cells and neurons than it typically would when the researchers synthesized neocortex cells from a human fetus to create the ancestral version. The same held true when they implanted the ancestor form of TKTL1 into brain organoids, tiny structures made from human stem cells that resemble the human brain.
Pinson and her team put mouse and ferret embryonic brains, either the human or ancestral version of TKTL1 to test this. The number of brain progenitor cells in the mice with the human gene was substantially higher. The fetal tissue produced fewer progenitor cells and neurons than it typically would when the researchers synthesized neocortex cells from a human fetus to create the ancestral version. The same held true when they implanted the ancestor form of TKTL1 into brain organoids, tiny structures made from human stem cells that resemble the human brain.






