Jumping Robots: Scientists Made Grasshopper-Like Material Can Jump 200 Times of Thickness
March 13, 2023 By Monica Green
(Image Credit Google)
Source: FuturoProssimo
Researchers at the University of Colorado Boulder have developed a new material that could give rise to soft robots capable of jumping 200 times above their thickness. This material takes inspiration from grasshoppers, one of the most astonishing leapers on Earth, which can leap into the air only up to 20 times their body lengths. This article delves deeper into this new technology and how it works.
The Discovery of the Jumping Material
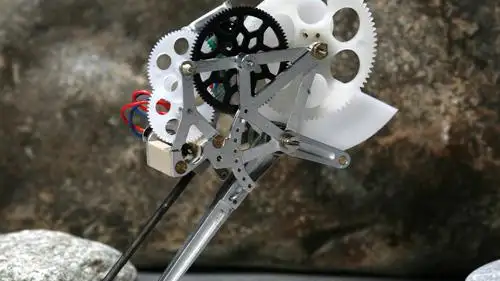
The rubber-like film is made up of liquid crystal elastomers (LCEs), special materials composed of cross-linked polymer networks. These exhibit properties of elastomers, used to make tires, adhesives, and soft robots, and liquid crystals, used to make TV displays, artificial muscles, and microbots. The study's first author, Tayler Hebner, and her colleagues were examining LCEs and their shape-changing ability when they observed an interesting behavior of LCEs. The researchers realized that LCEs are responsive to heat, which led to the development of the grasshopper-like material.
Source: New Scientist
How the Material Jumps
The grasshopper-like material is composed of three elastomer layers and liquid crystals. When the material is heated, the elastomer layers start shrinking, but the rate of shrinking is faster in the upper two layers, which are less rigid than the bottom layer. Meanwhile, the liquid crystals also start contracting. As a result of these disproportional changes, a cone-like formation appears near the legs on the backside of the robot's body. The robot has four legs attached to its four corner sides: two short legs in the front and two long legs in the backside. According to the researchers, as compared to the short legs, the longer back legs offer a higher point of contact, causing the snap-through force to lift the material at the desired angle.
A large amount of energy gets stored in the cone, which leads to mechanical instability in the film. As the LCE is further heated, the cone-shaped formation rapidly inverts, and the material gets kicked up in the air. The researchers claim they can change the configuration of their jumping material such that it leaps on cooling instead of heating. Plus, they can easily control the direction in which the material jumps by changing the alignment of its legs.
Potential Uses for LCEs
Hamed Shahsavan, a materials science expert at the University of Waterloo who wasn't involved in the study, suggests that such LCEs could be used to make a variety of mobile soft robots and devices. Confined jumping provides a large amount of energy output density that can be harvested for the load-bearing functionality of small-scale soft robots. Jumping can also be utilized for the locomotion of small robots on uneven terrains, either directly or as a mechanism auxiliary to other locomotion mechanisms such as walking, crawling, inching, etc.
Science Advances, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.ade1320 (About DOIs)
The discovery of LCEs and their extraordinary jumping skills opens up new possibilities in material science and soft robotics. With this technology, future robots could push the limits of non-human biology. The grasshopper-like material could provide a potent means of mobility for soft robotics and could be used to make a variety of mobile soft robots and devices. Overall, LCEs are stronger, more flexible, and better actuators than conventional elastomers, making them ideal for use in soft robotics.


 Source: New Scientist
Source: New Scientist






